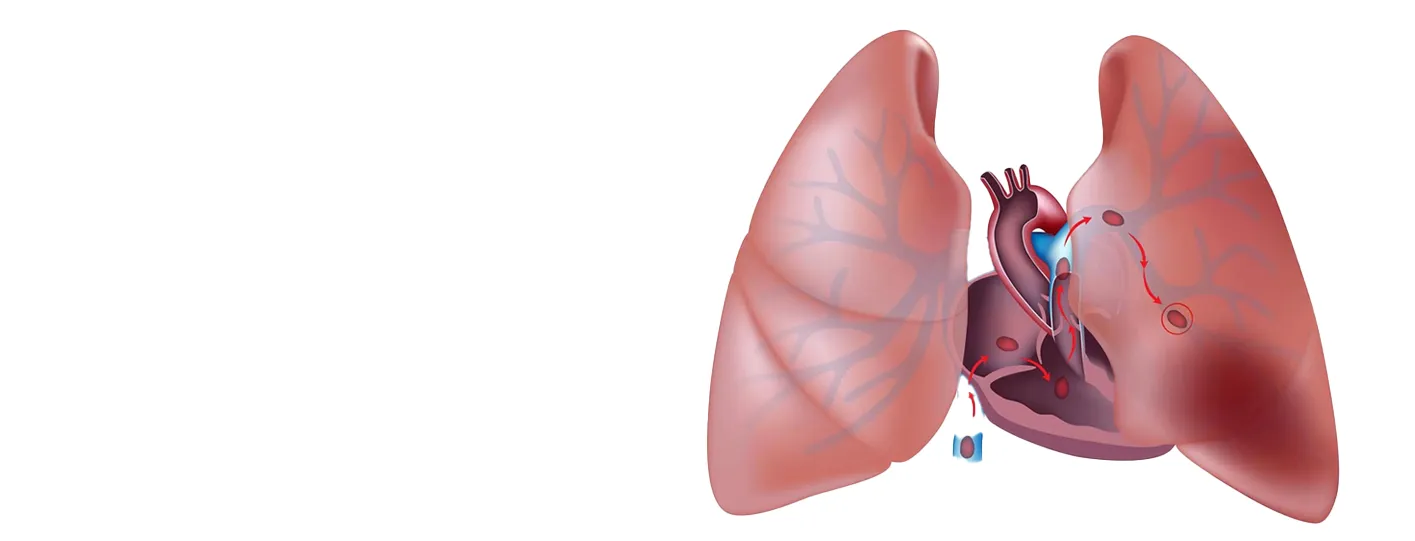
A thromboembolic disorder (also known as thromboembolism) happens when a blood clot (thrombus) forms in a blood vessel, breaks loose, and flows through the bloodstream, becoming an embolus. This then blocks another blood vessel, blocking blood flow to vital organs, leading to damage.
Types of Thromboembolic Disorders (Thromboembolism)
There are mainly two types of thromboembolism:
1. Venous Thromboembolism (VTE)
It means the formation of blood clots in the veins.
This general term includes two related conditions:
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): A blood clot that develops in a deep vein, commonly in the legs.
- Pulmonary Embolism (PE): It is a life-threatening condition that happens if a part of the DVT breaks off and travels to the lungs. This can block an artery leading to ischemic stroke (a blood clot blocks an artery supplying blood to the brain) or myocardial infarction.
2. Arterial Thromboembolism
This can happen when a blood clot forms in an artery. This carries the risk of a heart attack or a stroke, depending on where the blockage occurs.
Early Signs of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
- Leg Pain and Tenderness
- Unexplained swelling in one leg, ankle, or foot
- Skin may become reddish, bluish, or darker
- Visible veins
Early Signs of Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
- Shortness of breath
- Sharp, stabbing chest pain
- Chest pain worsens with deep breaths, coughing, or movement
- Rapid heartbeat
- Blood-streaked mucus or sputum
- Dizziness or fainting
- Excessive sweating
Early Signs of Arterial Thromboembolism
- Sudden, severe cramping pain in the arm or leg
- Coldness
- Pallor (pale skin)
- Numbness, weakness, or absent pulse
Risk factors for thromboembolism
The risk factors for thromboembolism can differ, depending on venous and arterial thromboembolism.
The following are the risk factors of deep venous thrombosis:
- Obesity
- Height
- May–Thurner illness
- Diet
- Tobacco
The following are the risk factors for arterial thromboembolism.
Thromboembolic Disorders Complications
The complication may depend on the complications, some of which are:
- Tissue necrosis and gangrene due to a lack of oxygen
- Acute myocardial infarction (heart attack)
- Paralysis, speech loss, confusion, or other neurological deficits.
- Organ failure
- Septic shock and infection
Treatment Options for Thromboembolism
The Best Cardiologist, after proper diagnosis, can prescribe the following treatment.
- Anticoagulants prevent existing clots from getting bigger and prevent the formation of new ones.
- Thrombolytics to dissolve severe, life-threatening clots.
- Mechanical Therapies like Catheter-Directed Thrombolysis, Percutaneous Thrombectomy/Embolectomy, or IVC Filters for severe cases.
- Supportive measures like Compression Stockings, Compression Devices, Pain Management, and lifestyle modifications (such as exercise, hydration, stress management, and quitting smoking).
Conclusion
Thromboembolism requires regular checks for bleeding or recurrent clots. If you experience unusual leg pain and tenderness, shortness of breath, and any other symptoms, immediately consult the best heart doctor near you. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent the condition from becoming severe.
Best Thromboembolic Disorders Treatment Hospital Near Me in Bikaner | Artemis Cardiac Care
Artemis Cardiac Care is known for comprehensive heart and blood vessel care, including thromboembolic disorders. Visit the best nearby heart doctor in Bikaner to prevent further complications.
Treatment Options Available:
- Non-Invasive Cardiology
- Interventional Cardiology
- Percutaneous Valvular
- Interventions
- Electrophysiology
- Pacemaker Implantation
- CRT, ICD & Combo Device Implantation
Call us at +91 9070902010 (24/7).
FAQs
Q1: What are the first signs of blood clots?
A: The signs may vary from person to person. However, it may generally involve pain, swelling, warmth, and redness in a limb, like a persistent calf cramp.
Q2: What is an example of a thrombotic disorder?
A: Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT), Pulmonary Embolism (PE), Arterial Thrombosis, and Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP) are some examples of thrombotic disorders.
Q3: Can dehydration cause blood clots?
A: Yes, lack of hydration can contribute to the increased risk of blood clots, because it causes your blood to get thicker than usual.