


An angiography is a type of imaging scan that uses X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans to visualize blood flow in your vessels. Coronary angiography allows healthcare specialists to examine your coronary arteries. Angioplasty, on the other hand, is a technique in which healthcare experts place balloons or stents into arteries in the heart to alleviate blockages and constriction. The two treatments are carried out in comparable ways.
An angiography is conducted with a tiny tube known as a catheter. A healthcare practitioner will insert the catheter through your arm or groin into an artery that leads to your heart. They will then inject contrast dye into the catheter to aid in the acquisition of images of the blood arteries in your heart using X-ray technology.
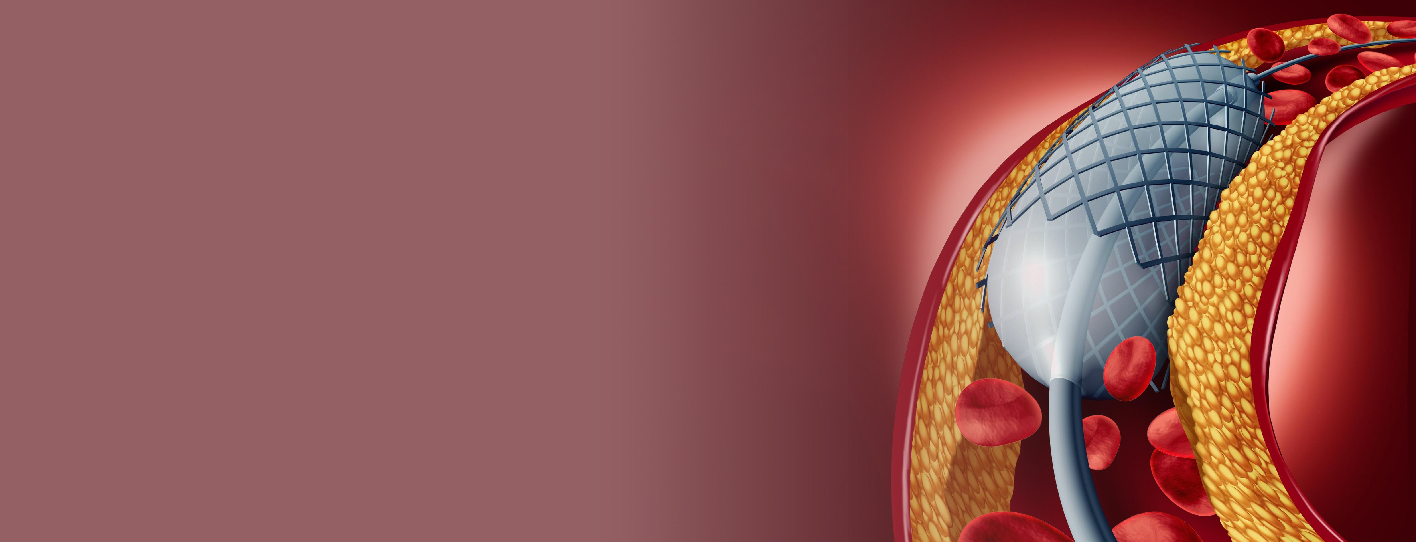
An angioplasty also entails inserting a catheter through an artery that leads to your heart. Instead of taking photos, a healthcare expert uses the catheter to implant a balloon or stent at the source of the obstruction. Once the device is implanted, the obstruction is flattened against the arterial wall, allowing blood to flow to your heart. An angiography could lead to an angioplasty. In some circumstances, healthcare practitioners use an angiogram to diagnose artery blockages before performing angioplasty.
Yes. Your doctor will order an angiography to examine the arteries in your heart. They will use it to collect images of any obstructions in your arteries. If they discover a blockage, angioplasty is one therapy option. In fact, your angiography may lead to an angioplasty in the same visit.
It is possible to do an angiography and an angioplasty simultaneously. A contemporaneous angiography and angioplasty (also known as PCI or percutaneous coronary intervention) is a common technique used when a patient has serious coronary artery blockages. During this simultaneous operation, an angiography is utilized to locate blockages, followed by angioplasty to unblock the blocked artery using a balloon or stent. This technique can help restore blood flow and alleviate the symptoms of coronary artery disease.
Angiography is a procedure used to assess the health of your blood arteries and how blood flows through them. It can assist identify or explore a variety of blood vessel issues, including:
The following steps take place during angiography:
The following are the different types of angiography:
Angioplasty, commonly known as balloon angioplasty, is a surgery that opens arteries to allow blood to pass through more readily. This minimally invasive method is used by healthcare practitioners in tight areas in arteries where plaque narrows or limits the space inside the artery. Angioplasty helps to treat the following conditions:
The following steps take place during angioplasty:
It's crucial to remember that everyone is unique, and there's no "right" or "wrong" response to which examination is best. Angiography provides an important assessment of the condition of your arteries, whereas angioplasty restores blood flow to obstructed arteries.
Ultimately, it is up to your doctor to choose which is best for you. If you or your loved ones are looking for the best cardiac treatment, schedule a consultation with us today. Get treated at Artemis Cardiac Care for the best cardiac care experience.
Q: Can angioplasty be performed without an angiogram?
A: Prior to your angioplasty, you may undergo an angiography. You will first undergo an angiography to examine your arteries and determine the location of the blockages. Sometimes your cardiologist will do the angiography first, then the angioplasty as part of the same surgery.
Q: Is there any age limit for angioplasty?
A: Angioplasty can be performed at any age, however the procedure's risks increase after the age of 80. The elderly individual frequently has other heart problems or health conditions that must be addressed.
Q: Which is better: angioplasty or angiography?
A: Angiography and angioplasty are two different medical procedures that involve blood arteries. While angiography is used to analyze or evaluate your blood vessels for possible heart disease, angioplasty includes expanding the restricted arteries to address the problem. Ultimately, it is up to your doctor to choose which is best for you.
Q: How many hours does angiography take?
A: The angiography takes around one to two hours to complete. Sometimes it takes longer. In certain cases, the interventional radiologist will do a second operation, such as an angioplasty, concurrently with the angiography, which leads to the procedure taking longer.
From Recent Advancements in Heart Care to Tips and Tricks to make your Heart Healthy Again, stay updated with reliable and informative blogs by our experts.