

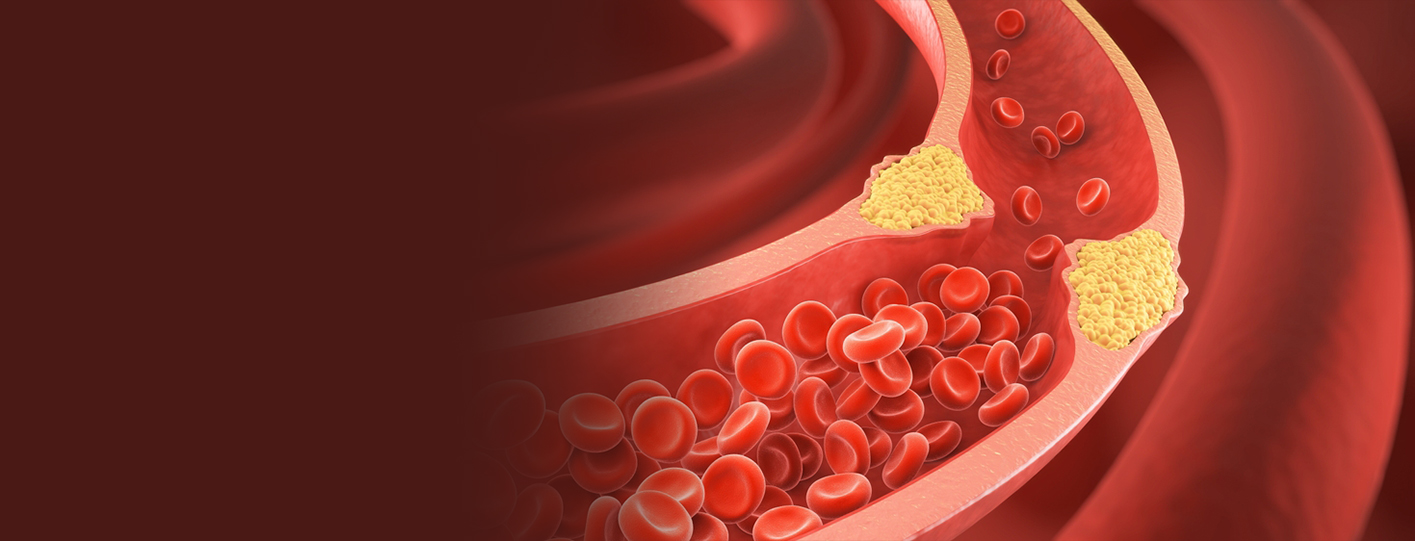

Cholesterol is a fatty substance found in your blood, essential for building cells and producing hormones. However, too much cholesterol, particularly low-density lipoprotein (LDL), commonly known as "bad cholesterol," can lead to plaque buildup in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease.
There are two main types of cholesterol:
An imbalance between LDL and HDL cholesterol can lead to serious cardiovascular complications.
Read Also: Heart Disease Explained: Signs, Symptoms, and How to Reduce Your Risk
One of the most dangerous aspects of high cholesterol is that it does not present any noticeable symptoms. It can silently cause damage over the years without showing warning signs until a major event, such as a heart attack or stroke, occurs. However, some indirect signs may indicate high cholesterol, including:
Regular cholesterol testing is the only sure way to determine if your cholesterol levels are high.
When there is excess LDL cholesterol in the bloodstream, it sticks to the walls of the arteries, forming plaques. Over time, these plaques narrow the arteries, a condition known as atherosclerosis, reducing blood flow to the heart and other organs.
As plaque builds up, it can rupture and form blood clots, blocking the flow of oxygen-rich blood to the heart. This can result in a heart attack, which can be fatal if not treated immediately.
Similarly, if a clot forms in an artery supplying blood to the brain, it can cause a stroke, leading to severe brain damage or death.
Narrowed arteries force the heart to pump harder, increasing blood pressure. High blood pressure further damages the arteries, creating a dangerous cycle that heightens the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Several factors contribute to high cholesterol, including:
Consuming foods high in saturated and trans fats, such as fried foods, processed meats, and baked goods, increases LDL cholesterol levels.
A sedentary lifestyle leads to weight gain and reduced levels of HDL (good cholesterol), making it easier for LDL cholesterol to accumulate in the bloodstream.
Excess body weight increases the likelihood of high cholesterol and other risk factors for heart disease, such as diabetes and hypertension.
Familial hypercholesterolemia is a genetic condition that causes extremely high cholesterol levels from birth, increasing the risk of early-onset heart disease.
Smoking damages blood vessels and lowers HDL cholesterol, while excessive alcohol intake can raise total cholesterol levels.
Conditions such as diabetes, hypothyroidism, and kidney disease can contribute to high cholesterol levels and increase cardiovascular risk.
CHD occurs when plaque buildup in the coronary arteries restricts blood flow to the heart. It can lead to chest pain (angina), heart attacks, and heart failure.
This refers to heart defects present at birth, which may be worsened by high cholesterol levels, especially if there is a family history of heart disease.
A severe congenital condition where the heart struggles to deliver enough oxygen to the body, potentially exacerbated by cholesterol-related blockages.
High cholesterol can cause blockages in arteries outside the heart, particularly in the legs, leading to pain, numbness, and mobility issues.
Managing high cholesterol involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medical treatments.
Adopting a heart-healthy diet is crucial for managing cholesterol levels. Increase your fiber intake by consuming more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while avoiding saturated fats and processed foods. Regular exercise also plays a vital role—engage in at least 30 minutes of moderate physical activity, such as walking or swimming, most days of the week.
Quitting smoking is another key step, as smoking cessation not only improves overall heart health but also helps raise good cholesterol levels. Additionally, limiting alcohol consumption is essential, as excessive intake can lead to cholesterol-related complications.
Several medications help manage high cholesterol and reduce the risk of heart disease. Statins are the most commonly prescribed drugs, effectively lowering LDL cholesterol and improving heart health. Bile acid sequestrants work by preventing the absorption of bile acids in the intestine, leading to lower cholesterol levels.
Cholesterol absorption inhibitors reduce the amount of cholesterol absorbed from food, further aiding in cholesterol control. For individuals with genetic high cholesterol or those who do not respond well to statins, PCSK9 inhibitors provide an alternative treatment option by significantly lowering LDL cholesterol levels.
In severe cases, medical procedures may be necessary:
Prevention is key to maintaining good heart health. Here are some tips to keep cholesterol levels in check and reduce heart disease risk:
A simple blood test can measure cholesterol levels, allowing early detection and management of high cholesterol before it leads to complications.
Losing even a small amount of weight can significantly lower cholesterol and reduce heart disease risk.
Chronic stress contributes to unhealthy eating habits and high blood pressure, both of which affect cholesterol levels.
Regular exercise helps maintain good cholesterol levels and keeps your heart strong.
Eat more omega-3 fatty acids (found in fish), nuts, and seeds while cutting back on processed and fried foods.
From Recent Advancements in Heart Care to Tips and Tricks to make your Heart Healthy Again, stay updated with reliable and informative blogs by our experts.